Introduction
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) piping has become one of the most widely used and reliable piping solutions in modern industry. With its high density, excellent abrasion resistance, chemical durability, flexibility, and long service life, HDPE is a preferred choice in a variety of applications.
Engineers rely on HDPE piping in large-scale water infrastructure projects, sewage systems, irrigation networks, and industrial facilities where robust performance is required under challenging outdoor and underground conditions.
Technical Properties
The following table summarizes typical material properties of HDPE:
| Parameter | Typical Value | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 0.94-0.96 | g/cm³ |
| Tensile Strength | 25-30 | MPa |
| Linear Thermal Expansion (α) | 0.15-0.20 | mm/m·K |
| Continuous Service Temperature | up to 60 | °C |
| Short-Term Exposure (no pressure) | up to ~82 | °C |
HDPE maintains flexibility even at sub-zero temperatures, making it ideal for outdoor installations in cold climates. Its limitation is in high-temperature applications, where strength and stability decrease beyond 60°C.
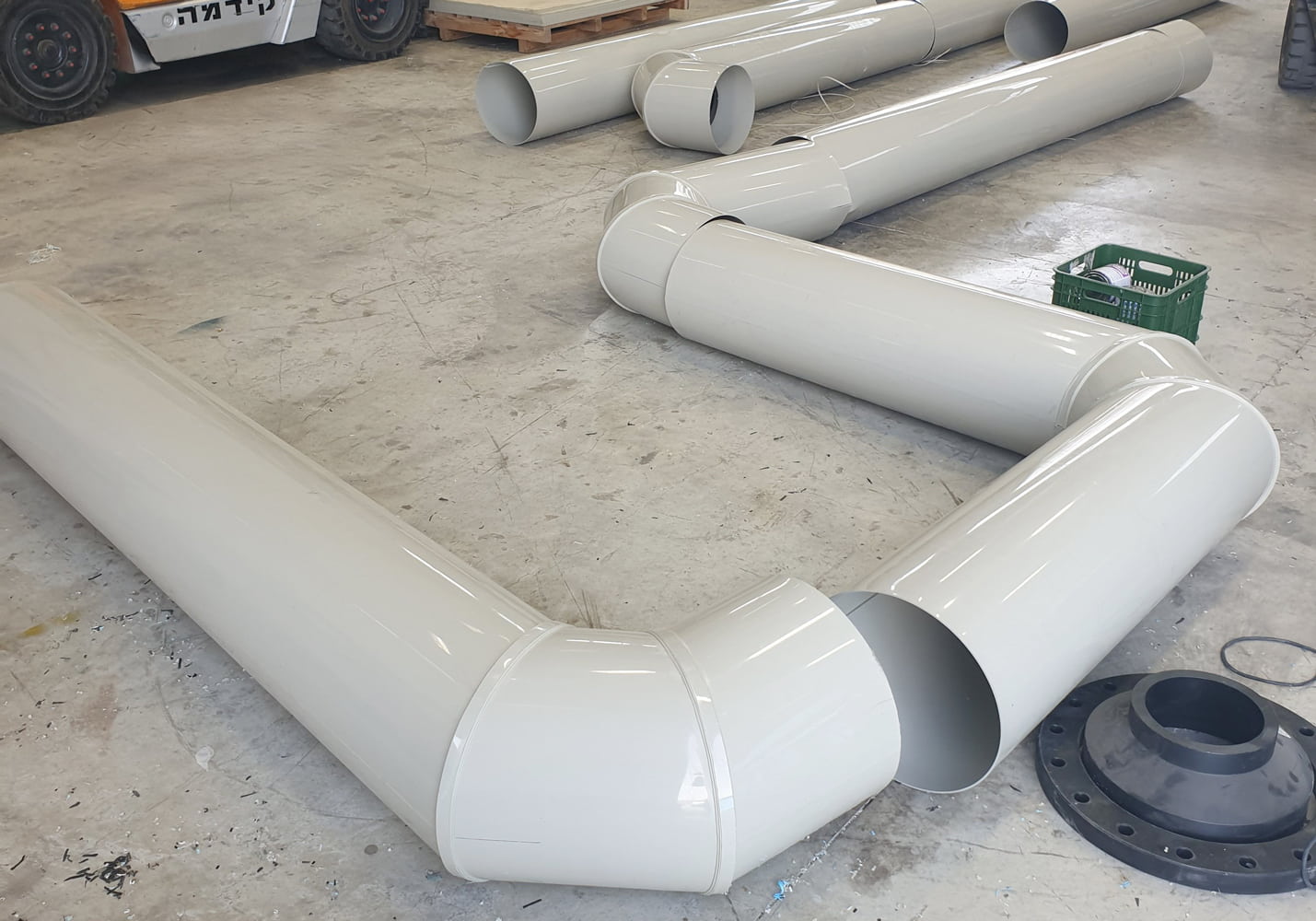
Dimensions and Pressure Ratings
HDPE pipes are available in a wide range of diameters, from DN20 up to DN1200, and in different pressure ratings (PN6-PN25).
| Outer Diameter (DN) | Wall Thickness - PN10 | Wall Thickness - PN16 |
|---|---|---|
| 32 mm | 3.0 mm | 4.4 mm |
| 90 mm | 8.2 mm | 13.4 mm |
| 160 mm | 14.6 mm | 23.2 mm |
| 400 mm | 36.3 mm | 58.8 mm |
Large-diameter HDPE pipes are especially common in municipal water and infrastructure projects.
Chemical Resistance
HDPE shows excellent resistance against many acids, bases, and salts, but is less suitable for aromatic solvents and halogenated hydrocarbons.
| Chemical | Typical Concentration | Service Temp | Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitric Acid | 30% | up to 50°C | Good |
| Sulfuric Acid | 30% | up to 50°C | Good |
| Caustic Soda (NaOH) | 20% | up to 60°C | Excellent |
| Free Chlorine | - | up to 25°C | Poor |
| Toluene / Gasoline | - | Ambient | Not Recommended |
Abrasion and Mechanical Strength
One of HDPE’s key advantages is its outstanding abrasion resistance. Comparative testing shows that HDPE outperforms PVC and even PP in abrasive flow environments.
| Material | Relative Wear (after 1000 hrs) |
|---|---|
| HDPE | 85% |
| PP | 100% (baseline) |
| PVC | 140% |
This makes HDPE particularly suitable for conveying water with sand, slurry, or suspended particles.
Temperature Range
HDPE pipes are designed for continuous service between -20°C and 60°C. In this range, they remain flexible and crack-resistant, which is crucial for outdoor and underground applications. At higher temperatures, mechanical properties degrade, making HDPE unsuitable for long-term hot water transport.
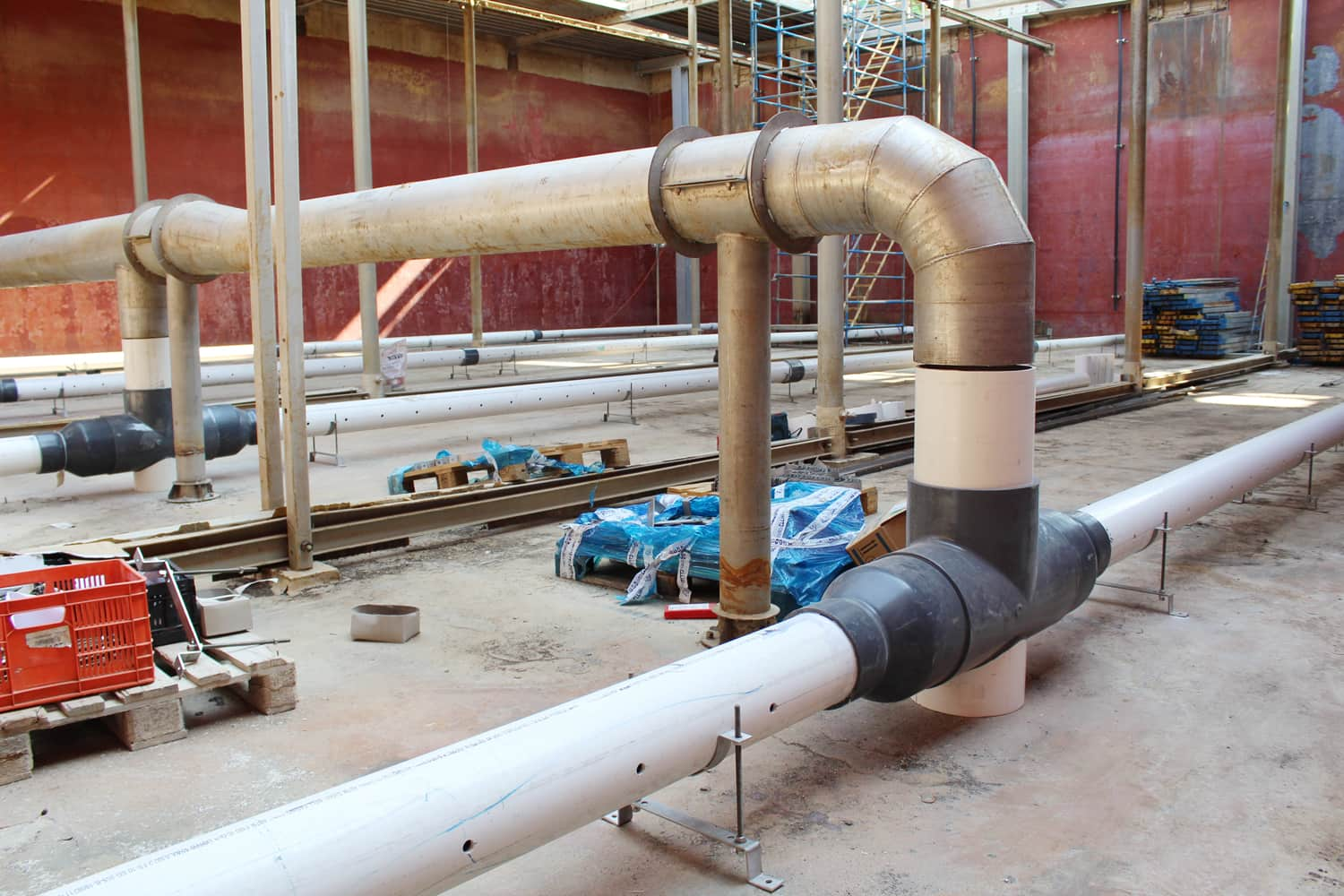
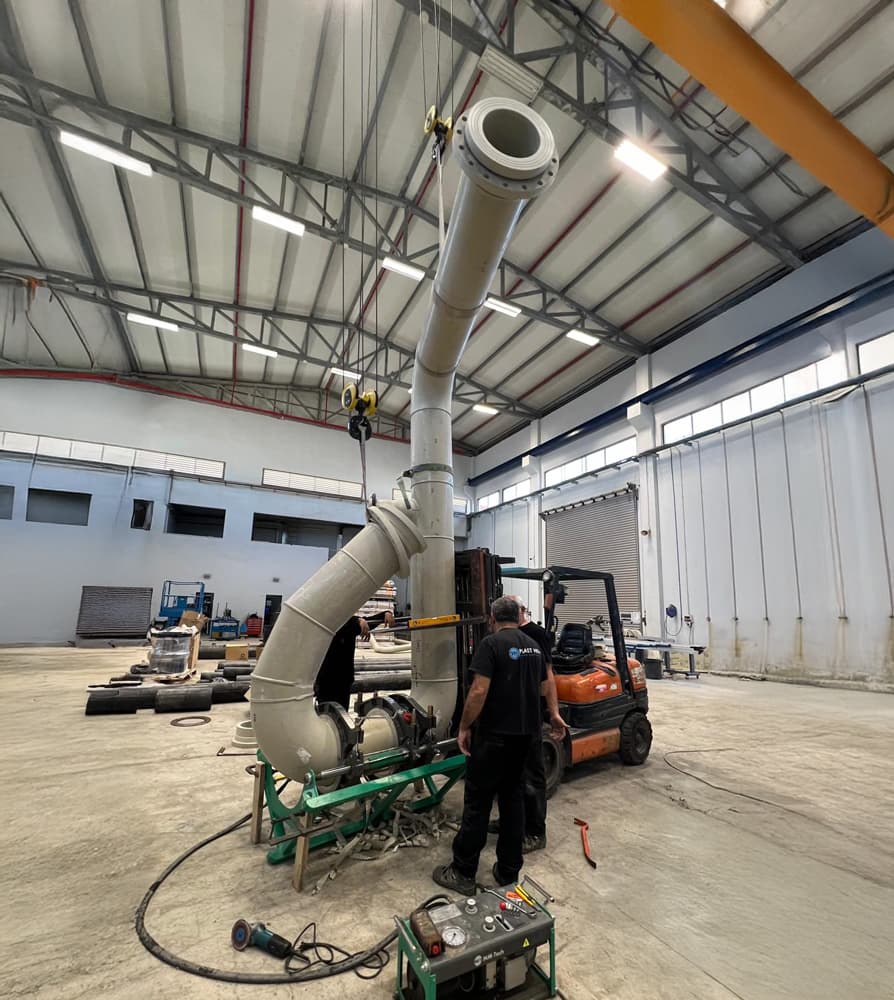
Installation and Joining Methods
HDPE pipes can be installed using:
- Butt Welding - ideal for large diameters and long runs.
- Electrofusion Welding - precise, strong joints with excellent pressure resistance.
- Mechanical Couplers - suitable for temporary setups and quick repairs.
In large projects, automatic welding machines are often used to ensure consistent joint quality.
Industrial Applications
HDPE piping is widely used across industries:
- Municipal and industrial water supply systems
- Sewage and drainage networks
- Agricultural irrigation systems
- Pumping stations and energy infrastructure
- Chemical industries handling corrosive fluids at low to medium temperatures
Key Advantages
- Superior abrasion and mechanical resistance
- Flexibility in low-temperature environments
- Lightweight and easy to transport/install
- Cost-effective in large-scale infrastructure projects
- Long service life (30+ years in properly designed systems)
Comparative Overview of Piping Materials
| Parameter | PP (Polypropylene) | PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) | HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) | PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride) | Metal (Stainless/Steel) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous Temp. | 0-90°C | 0-60°C | -20-60°C | -40-140°C | Up to 200°C+ |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Good | Very good | Excellent | Good, corrosion-prone |
| Mechanical Strength | Medium | Medium | Relatively high | Very high | Very high |
| Weight | Light | Light | Very light | Medium | Heavy |
| Installation | Easy, welding/threads | Easy, glued/threads | Easy, welding/threads | Requires advanced tools | Complex, metal welding |
| Cost | Low | Very low | Low | High | Very high |
| Service Life | 25-30 years | 15-20 years | 25-30 years | 30+ years | 30+ years |
| UV Resistance | Moderate | Very poor | Very poor | Good | Good |
Conclusion
HDPE piping is a robust, versatile, and cost-effective solution for engineers working on infrastructure, water systems, and industrial projects. Its unique balance of abrasion resistance, chemical durability, and installation flexibility makes it one of the most reliable piping systems available today.